Mexico has increased its use of advanced manufacturing cobots, according to the US Department of Commerce.
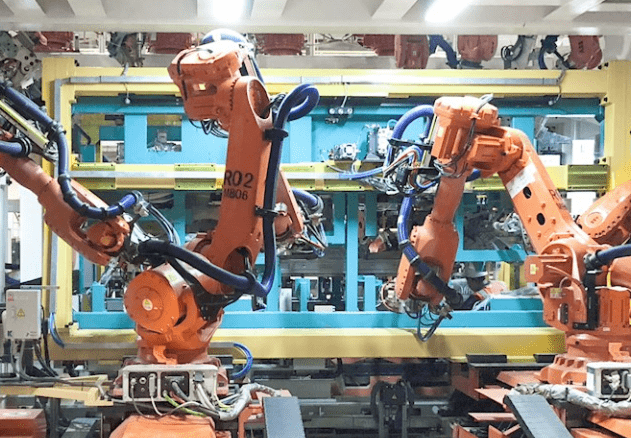
A cobot is a collaborative robot designed to work alongside people in industrial environments. It performs repetitive or precise tasks, improves productivity, reduces occupational hazards, and integrates easily into production lines without complex barriers.
Advanced manufacturing cobots
In the first 10 months of 2025, Mexican exports of goods to the United States totaled $447.998 billion, representing a year-on-year increase of 5.6%. Of that amount, 27.1% corresponded to advanced technology products.
Collaborative robots, or cobots, work alongside humans in industrial processes. From the outset, they have stood out for taking on repetitive and risky tasks. For example, they are used in welding, assembly, and lifting, while helping to protect personnel and improve operational efficiency.
In addition, the incorporation of cobots in manufacturing drives efficiency gains and enhances workplace safety. Unlike traditional robots, they integrate sensors and artificial intelligence. As a result, they recognize human interactions and adjust their pace and direction according to worker participation.
Cobots are often linked to production management systems. This allows them to share information in real time and facilitates data integration and optimization. At the same time, the global market is expected to grow to $6.8 billion by 2029.
Automotive industry
In Mexico, although their use is less widespread than in the United States, cobots are already present in several industries. The automotive industry accounts for 70% of installed units, with around 4,087 cobots employed in production lines and machinery maintenance.
The Mexican chemical industry has 289 units, equivalent to 7%, while the electronics industry has 276, or about 5%. And the remaining 18% is distributed among logistics, agriculture, construction, and healthcare, gradually expanding their sectoral adoption.
Import statistics do not specify whether industrial robots are collaborative, but they do offer an idea of the origin of the products currently imported into Mexico.
Of these imports, 30% come from China, 16% from Japan, 14% from the United States, and 40% from other countries. Marketing is carried out through local distributors with installation and support services.